The shift functionality
Overview
The Opinum Data-hub allows to define a shift on data sources for Pie charts, Time series, Value tiles and Correlation tiles.
Defining a shift on a data source allows to offset the time frame for which data will be retrieved from the data source. A shift with a value of '0' means the query will retrieve data for the time frame set on the tile.
A data source with a shift other than'0' means that the system will deduce the period defined in the shift from the original time frame selected. The resulting time frame will be used in the query on that data source.
E.g.: assuming the current date is 23-09-2019 and a time series with a ‘relative – past – 1 month’ is configured. A data source with a 1-month shift is added.
The initial time frame would be August 2019 (01-08 to 31-08). However, because of the shift, data from July 2019 (from 01-07 to 31-07) are shown.
This functionality allows to compare data from one data source for different periods (e.g.: current month compared to previous month).
It also adds flexibility to the definition of the time frame, allowing the display of data from a rolling period in the past which could not be defined using the available time frame settings.
E.g.: using a 2-month shift in September 2019 would allow to display the average consumption from two months earlier (July 2019). In October, the same graph will display the average for August, and so on.
Shift on different time frames
The principle used is the same for all the types of time frames. The period defined in the shift will be deduced from the original time frame selected.
Shift on absolute time frame
Absolute time frames allow to pick a precise date range. The shift will be then applied to this range.
E.g. : Assuming a pie chart with an absolute time frame from '16-01-2018' to '16-07-2018' is configured:
A shift of 1 month will show the data from '16-12-2017' to '16-06-2018'.
A shift of 1 year will show the data from '16-01-2017' to '16-07-2017'.
A shift of 1 week will show the data from '09-01-2018' to '09-07-2018'.
Shift on relative time frames
Below, you will find example of shift applied to relative time frames
Past period
E.g. : Assuming the current date is '01-10-2019'. A time series with a 'relative - past period - 1 Last Week' is configured.
The original time frame is : from '23-09-2019' to '29-09-2019'.
A shift of 1 hour will show the data for the period '22-09-2019 23:00' to '29-09-2019 23:00'
A shift of 2 weeks will show the data for the period '09-09-2019' to '15-09-2019'
Past and current period
E.g. : Assuming the current time is '01-10-2019 13:00:00'. A time series with a 'relative - past & current period- 5 Last days and current' is configured.
The original time frame is : from '26-09-2019 00:00' to '01-10-2019 13:00'.
A shift of 1 month will show the data for the period '26-08-2019 00:00' to '01-09-2019 13:00'.
A shift of 10 days will show the data for the period '16-09-2019 00:00' to '21-09-2019 13:00'.
Current period
E.g. : Assuming the current time is '01-10-2019 13:00:00'. A time series with a 'relative - current period - this month' is configured.
The original time frame is : from '01-10-2019 00:00' to '01-10-2019 13:00:00'.
A shift of 1 day will show the data for the period '30-09-2019 00:00' to '30-09-2019 13:00'.
A shift of 2 years will show the data for the period '01-10-2017 00:00' to '01-10-2017 13:00'.
Shift on different graphic types
Pie Chart
Shifts on pie charts allow, for example, to compare several months (or days, weeks, years).
The following chart displays the sum of one variable's data for the current month, the previous month, two months ago and three months ago, displayed as a percentage.
Value tile
Shifts on value tiles allow, for example, to display the value for a period in the past (year, month, week, day, ...) that cannot be set with the relative time frames that are available (e.g. : average consumption of two months ago).
You can also compare the same data at different times:
Correlation tile
Shifts on correlation tiles allow to display the correlation between variables for a period in the past and to compare these correlated variables for different periods (e.g. : current year and last year).
Time series
This type of graphic has two particularities. The first one is that it displays data over time.
The second is that it allows to change the granularity of the data (drill down) displayed through a zoom. For example, if data are displayed by year and, clicking on data '2017' will automatically display monthly data for 2017.
Tip
Learn more about Time series
Displaying
In order to compare data easily, the displaying works as followed : the time axe is created based on the data source with the minimum shift. If there are other data sources with greater shifts, there are displayed next to the first one.
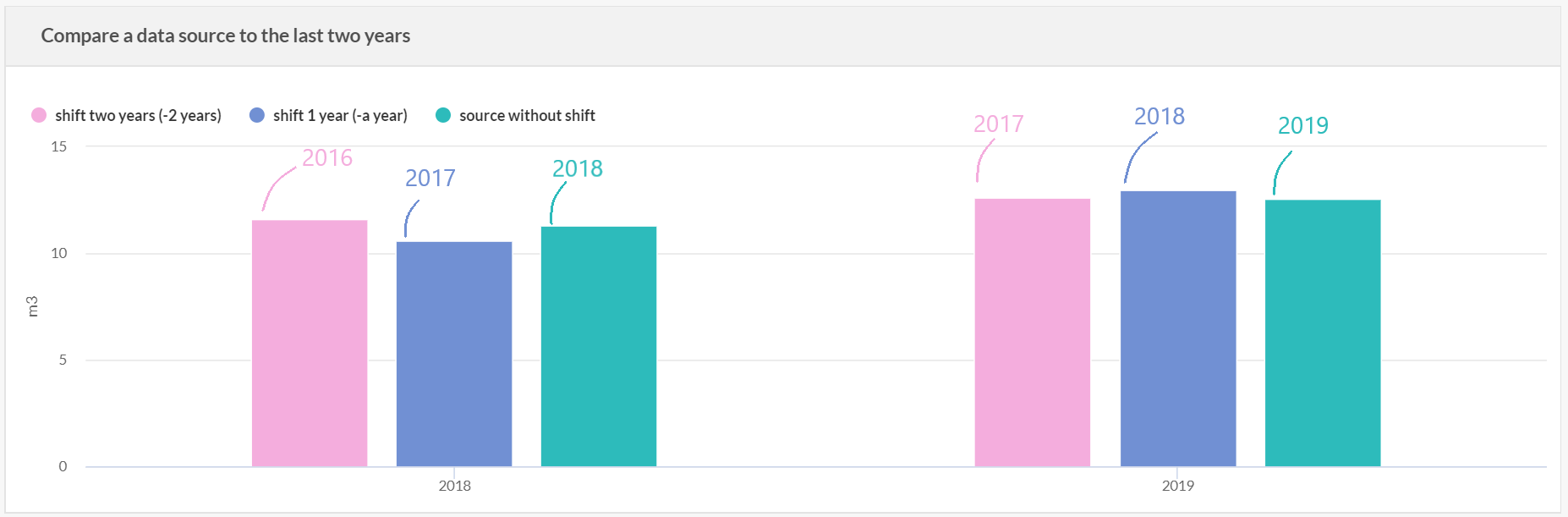
E.g.: A time series displayed by year with a data source containing data from '15-05-2018 to 20-09-2019' (shift 0) is created.
This data source is duplicated twice : with a shift of 1 year (from '15-05-2017 to 20-09-2018') and with a shift of 2 years (from '15-05-2016 to 20-09-2017').
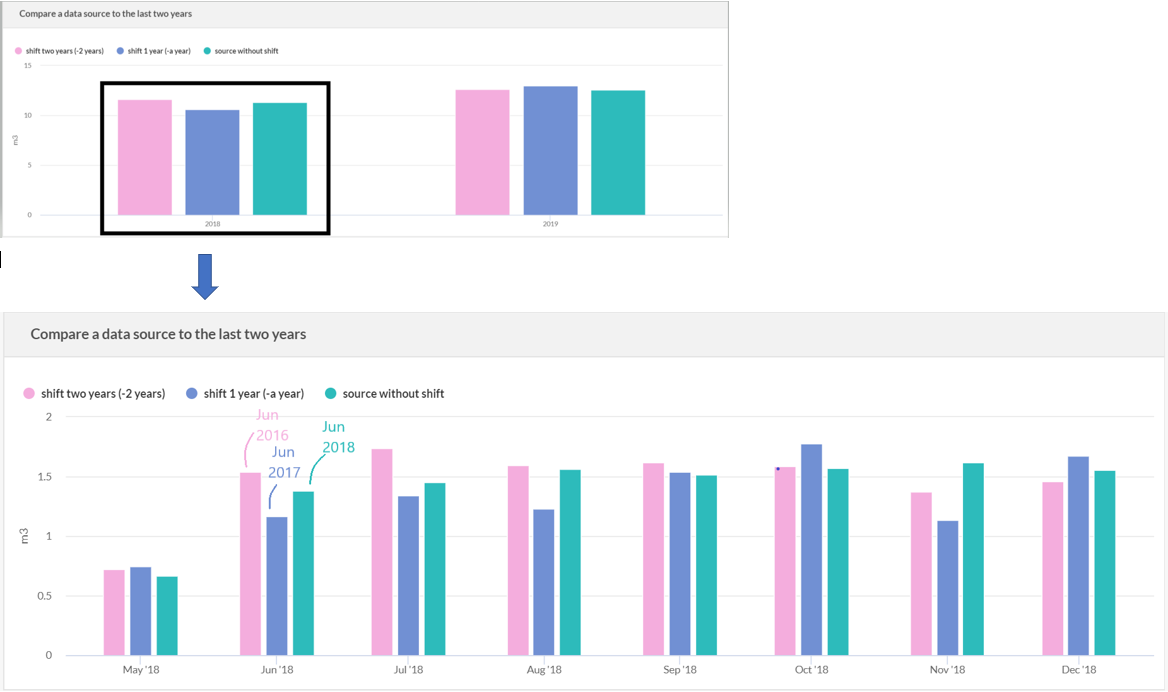
The axe of x on the time series, will displayed data for 2018 and 2019. The data shifted will displayed as followed :
Note
For the moment, on time series, the shift's granularity has to be the same that the tile's granularity.
If a time series is displayed by years, the shift applied has to be in years. A time series displayed by month and a data source with a shift of 1 week won't be correctly displayed.
Change of the granularity
The change of the granularity doesn't impact the shift. When clicking on a year to displayed it by months, for example, the exact same period is displayed. The only modification is the way to display it.
In our last example, clicking on data from 2018 will display the exact same data by months :